Nuclear Medicine in Berlin
Comprehensive medical care

Your Checklist – for a pleasant stay
-
1 Preparations
Describe your concerns and send the necessary documents to the hospital.
-
2 Relevant documents
Inform yourself about your medical visa and select all documents.
-
3 Stay
Inform yourself in time about your hospital and a appropriate accommodation.
-
4 After discharge
Verify if you will need a medication or further treatment.
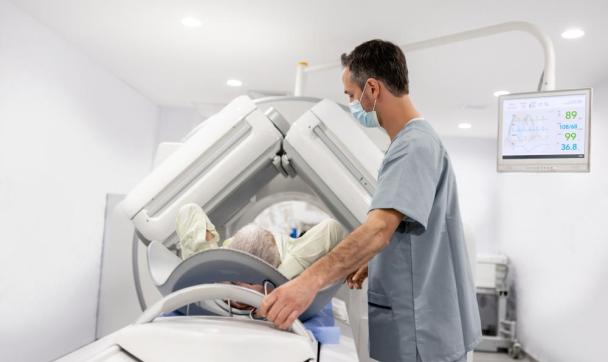
Nuclear medicine is an innovative medical specialty that uses radiolabelled substances to obtain highly precise information about organ function. Unlike purely structural imaging techniques such as CT or MRI, nuclear medicine focuses primarily on assessing the function of organs and tissues—often revealing abnormalities long before physical changes become visible.
A typical nuclear medicine procedure is thyroid scintigraphy, where a mildly radioactive tracer is injected into a vein. Just minutes later, a specialised gamma camera records the thyroid’s activity. Other commonly performed nuclear medicine scans include skeletal scintigraphy, myocardial scintigraphy (heart), renal scintigraphy, and pulmonary scintigraphy. Advanced hybrid imaging technologies such as SPECT/CT or PET/CT combine functional and anatomical imaging in a single device. This enables accurate localisation of tumours, metastases, and inflammation—crucial in the management of cancers such as prostate cancer, neuroendocrine tumours, or lymphomas.
In addition to diagnostics, nuclear medicine also offers targeted therapies. These include radioiodine therapy for benign and malignant thyroid conditions, PSMA radioligand therapy for metastatic prostate cancer, peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) for neuroendocrine tumours, selective internal radiation therapy (SIRT) for liver tumours and metastases, mIBG therapy for neuroblastoma, and radiosynoviorthesis (RSO) to relieve joint inflammation caused by rheumatic diseases such as osteoarthritis and arthritis.